publications
Below are selected publications in reversed chronological order. For the complete list, please vist my Google Scholar Profile.
2025
- IEEE TEVC
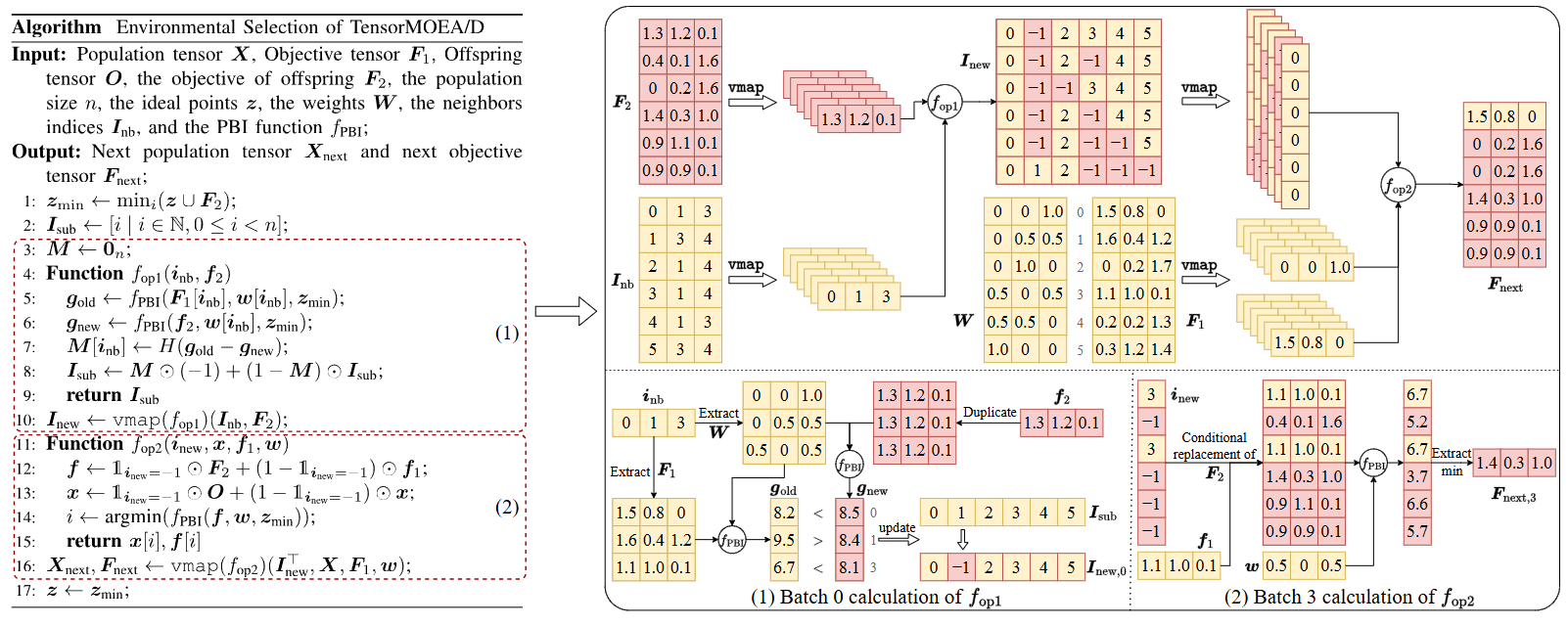 Bridging Evolutionary Multiobjective Optimization and GPU Acceleration via TensorizationZhenyu Liang, Hao Li, Naiwei Yu, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2025
Bridging Evolutionary Multiobjective Optimization and GPU Acceleration via TensorizationZhenyu Liang, Hao Li, Naiwei Yu, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2025Evolutionary multiobjective optimization (EMO) has made significant strides over the past two decades. However, as problem scales and complexities increase, traditional EMO algorithms face substantial performance limitations due to insufficient parallelism and scalability. While most work has focused on algorithm design to address these challenges, little attention has been given to hardware acceleration, thereby leaving a clear gap between EMO algorithms and advanced computing devices, such as GPUs. To bridge the gap, we propose to parallelize EMO algorithms on GPUs via the \emphtensorization methodology. By employing tensorization, the data structures and operations of EMO algorithms are transformed into concise tensor representations, which seamlessly enables automatic utilization of GPU computing. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach by applying it to three representative EMO algorithms: NSGA-III, MOEA/D, and HypE. To comprehensively assess our methodology, we introduce a multiobjective robot control benchmark using a GPU-accelerated physics engine. Our experiments show that the tensorized EMO algorithms achieve speedups of up to 1113x compared to their CPU-based counterparts, while maintaining solution quality and effectively scaling population sizes to hundreds of thousands. Furthermore, the tensorized EMO algorithms efficiently tackle complex multiobjective robot control tasks, producing high-quality solutions with diverse behaviors. Source codes are available at \urlhttps://github.com/EMI-Group/evomo.
- IEEE TEVC
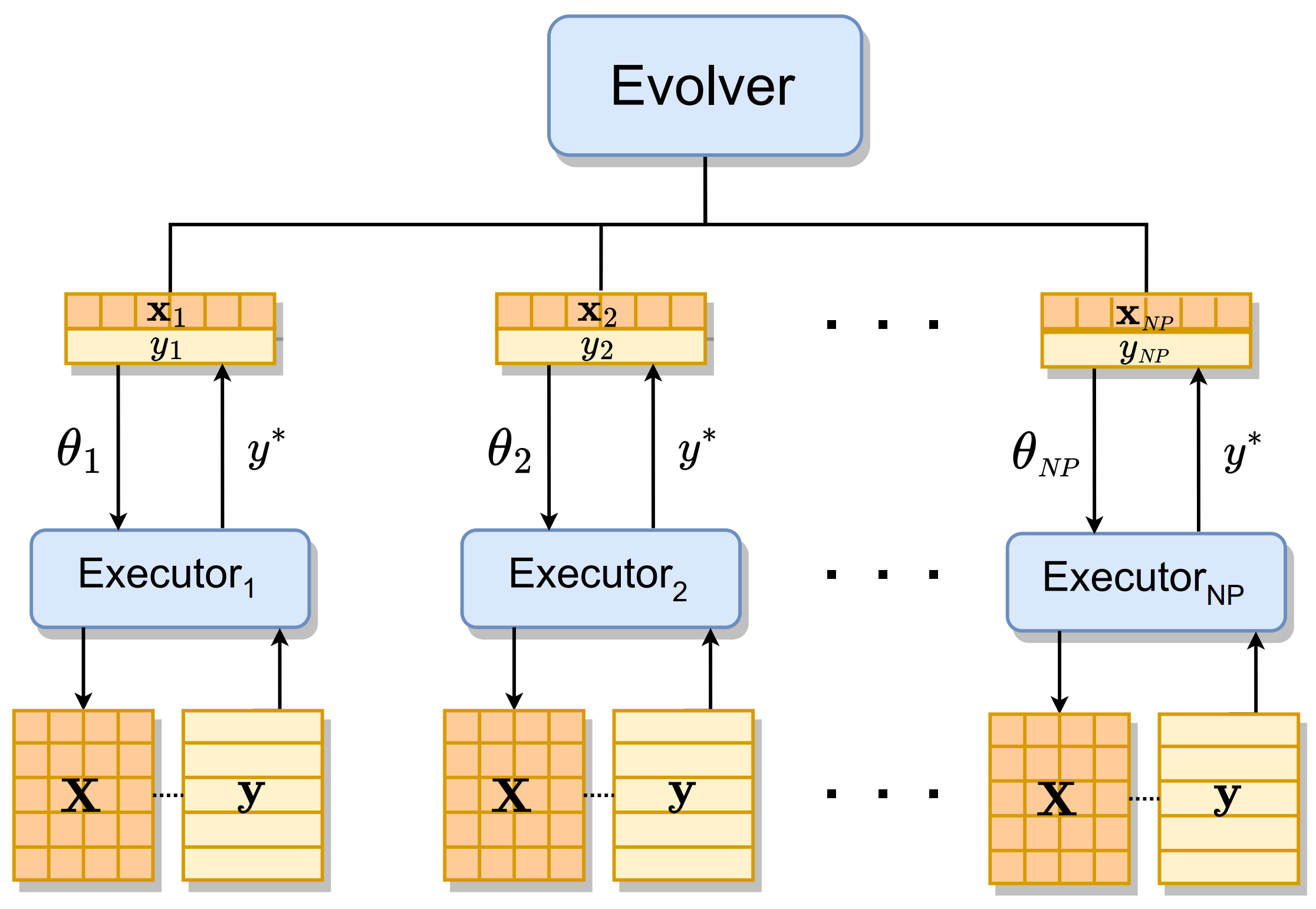 MetaDE: Evolving Differential Evolution by Differential EvolutionMinyang Chen, Chenchen Feng, and Ran ChengIEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2025
MetaDE: Evolving Differential Evolution by Differential EvolutionMinyang Chen, Chenchen Feng, and Ran ChengIEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2025As a cornerstone in the Evolutionary Computation (EC) domain, Differential Evolution (DE) is known for its simplicity and effectiveness in handling challenging black-box optimization problems. While the advantages of DE are well-recognized, achieving peak performance heavily depends on its hyperparameters such as the mutation factor, crossover probability, and the selection of specific DE strategies. Traditional approaches to this hyperparameter dilemma have leaned towards parameter tuning or adaptive mechanisms. However, identifying the optimal settings tailored for specific problems remains a persistent challenge. In response, we introduce MetaDE, an approach that evolves DE’s intrinsic hyperparameters and strategies using DE itself at a meta-level. A pivotal aspect of MetaDE is a specialized parameterization technique, which endows it with the capability to dynamically modify DE’s parameters and strategies throughout the evolutionary process. To augment computational efficiency, MetaDE incorporates a design that leverages parallel processing through a GPU-accelerated computing framework. Within such a framework, DE is not just a solver but also an optimizer for its own configurations, thus streamlining the process of hyperparameter optimization and problem-solving into a cohesive and automated workflow. Extensive evaluations on the CEC2022 benchmark suite demonstrate MetaDE’s promising performance. Moreover, when applied to robot control via evolutionary reinforcement learning, MetaDE also demonstrates promising performance. The source code of MetaDE is publicly accessible at: https://github.com/EMI-Group/metade.
2024
- IEEE TEVC
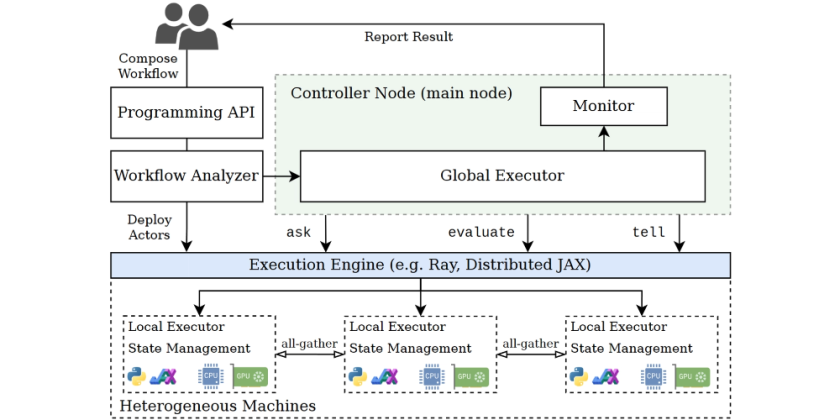 EvoX: A Distributed GPU-accelerated Framework for Scalable Evolutionary ComputationBeichen Huang, Ran Cheng, Zhuozhao Li, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2024
EvoX: A Distributed GPU-accelerated Framework for Scalable Evolutionary ComputationBeichen Huang, Ran Cheng, Zhuozhao Li, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2024Inspired by natural evolutionary processes, Evolutionary Computation (EC) has established itself as a cornerstone of Artificial Intelligence. Recently, with the surge in data-intensive applications and large-scale complex systems, the demand for scalable EC solutions has grown significantly. However, most existing EC infrastructures fall short of catering to the heightened demands of large-scale problem solving. While the advent of some pioneering GPU-accelerated EC libraries is a step forward, they also grapple with some limitations, particularly in terms of flexibility and architectural robustness. In response, we introduce EvoX: a computing framework tailored for automated, distributed, and heterogeneous execution of EC algorithms. At the core of EvoX lies a unique programming model to streamline the development of parallelizable EC algorithms, complemented by a computation model specifically optimized for distributed GPU acceleration. Building upon this foundation, we have crafted an extensive library comprising a wide spectrum of 50+ EC algorithms for both single-and multi-objective optimization. Furthermore, the library offers comprehensive support for a diverse set of benchmark problems, ranging from dozens of numerical test functions to hundreds of reinforcement learning tasks. Through extensive experiments across a range of problem scenarios and hardware configurations, EvoX demonstrates robust system and model performances. EvoX is open-source and accessible at: https://github.com/EMI-Group/EvoX.
2023
- IEEE TEVC
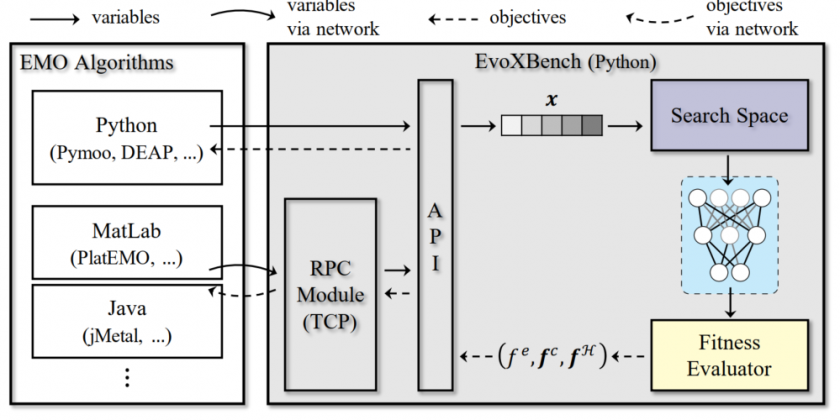 Neural Architecture Search as Multiobjective Optimization Benchmarks: Problem Formulation and Performance AssessmentZhichao Lu, Ran Cheng, Yaochu Jin, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2023
Neural Architecture Search as Multiobjective Optimization Benchmarks: Problem Formulation and Performance AssessmentZhichao Lu, Ran Cheng, Yaochu Jin, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2023The ongoing advancements in network architecture design have led to remarkable achievements in deep learning across various challenging computer vision tasks. Meanwhile, the development of neural architecture search (NAS) has provided promising approaches to automating the design of network architectures for lower prediction error. Recently, the emerging application scenarios of deep learning (e.g., autonomous driving) have raised higher demands for network architectures considering multiple design criteria: number of parameters/weights, number of floating-point operations, inference latency, among others. From an optimization point of view, the NAS tasks involving multiple design criteria are intrinsically multiobjective optimization problems; hence, it is reasonable to adopt evolutionary multiobjective optimization (EMO) algorithms for tackling them. Nonetheless, there is still a clear gap confining the related research along this pathway: on the one hand, there is a lack of a general problem formulation of NAS tasks from an optimization point of view; on the other hand, there are challenges in conducting benchmark assessments of EMO algorithms on NAS tasks. To bridge the gap: 1) we formulate NAS tasks into general multiobjective optimization problems and analyze the complex characteristics from an optimization point of view; 2) we present an end-to-end pipeline, dubbed EvoXBench , to generate benchmark test problems for EMO algorithms to run efficiently—without the requirement of GPUs or Pytorch/Tensorflow; and 3) we instantiate two test suites comprehensively covering two datasets, seven search spaces, and three hardware devices, involving up to eight objectives. Based on the above, we validate the proposed test suites using six representative EMO algorithms and provide some empirical analyses. The code of EvoXBench is available at https://github.com/EMI-Group/EvoXBench.